After reading Part I, you have a running DC/OS “cluster”, the dashboard UI ready for exploration. Now let’s talk about how to deploy service there. DC/OS management component runs on master nodes, so to-be-deployed services will run on agent nodes.
Agent Nodes – Public/Private Nodes
If you click “Nodes” on dashboard UI, you will see there are two agent nodes.
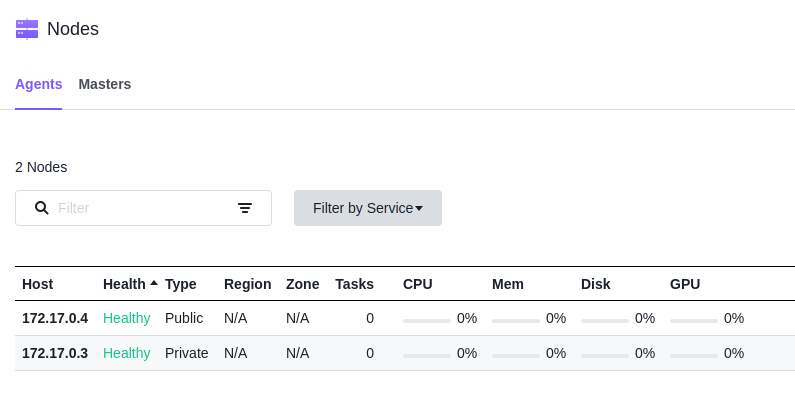
One is a private node, the other is an public one. A DC/OS agent node is a node on which user tasks are run. Agent nodes contain a few DC/OS components, including a Mesos agent process. Agent nodes can be public or private, depending on agent and network configuration.
- A private agent node is an agent node that is on a network that does not allow access from outside of the cluster via the cluster’s infrastructure networking.
- A public agent node is an agent node that is on a network that allows access from outside of the cluster via the cluster’s infrastructure networking.
More details about node types can be found here.
Deploy a Nginx Service with GUI
There two ways to deploy service – using GUI and using CLI. Let’s try GUI first and DC/OS CLI will be in later chapter.
Click “Services” on navigation bar, click “Run a service”, then click “Single Container”.
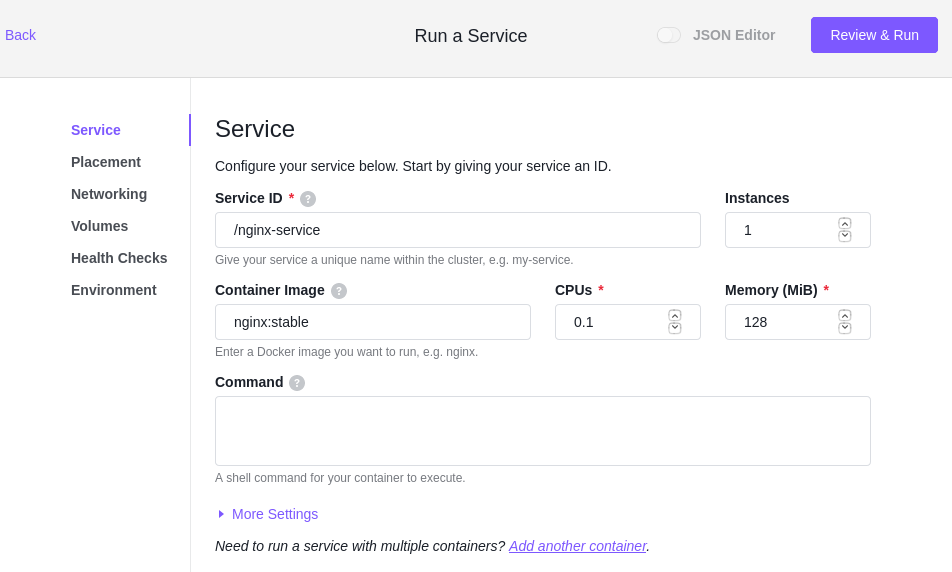
Now the container configuration UI shows up. Let’s do minimum configuration and bright up a nginx server.
On Service page
You need to define the service name, the container type (better to use “docker” with minidcos docker. With real cluster, you can use UCR), the image, how many instances, how much CPU/memory/GPU/disk and etc.
On Networking Page
Select “Bridge”, type the container’s port and service endpoint name (for service discovery), and enable the “Load Balanced Port” (Will talk about it in later chapters).
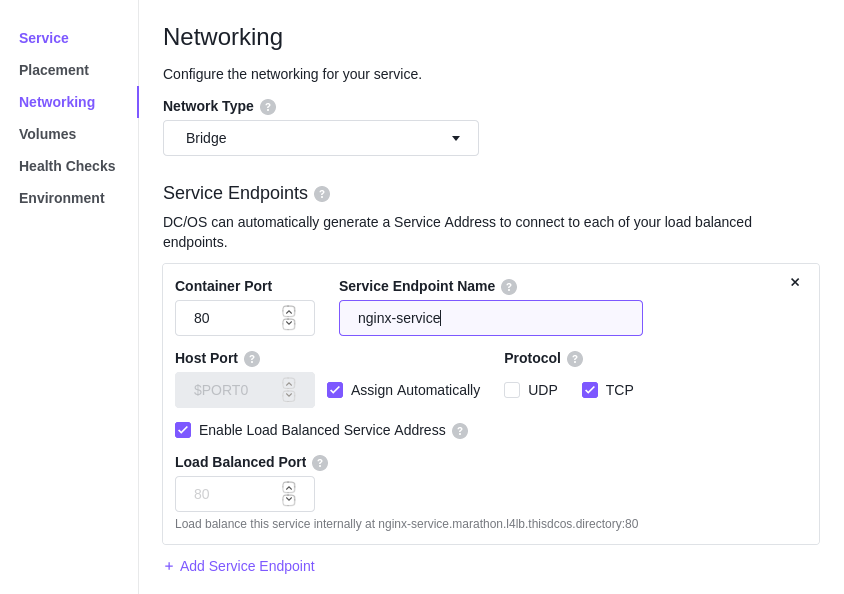
More details about DC/OS networking can be found here.
Other Pages
- Placements – Specify more constraints and tell DC/OS (underlying, it’s Marathon) to deploy the service on which node.
- Volumes – Specify a volume to mount to your service.
- Health Checks – Specify endpoints for health checking. DC/OS will periodically check the health of services. Details are here.
- Environment – Specify the environment variables (used by launching your services) or labels (expose more information to other services).
JSON Editor
You can enable JSON editor to review all the configuration in JSON format. The JSON file can also be used by DC/OS CLI, which allows us to version the configuration.
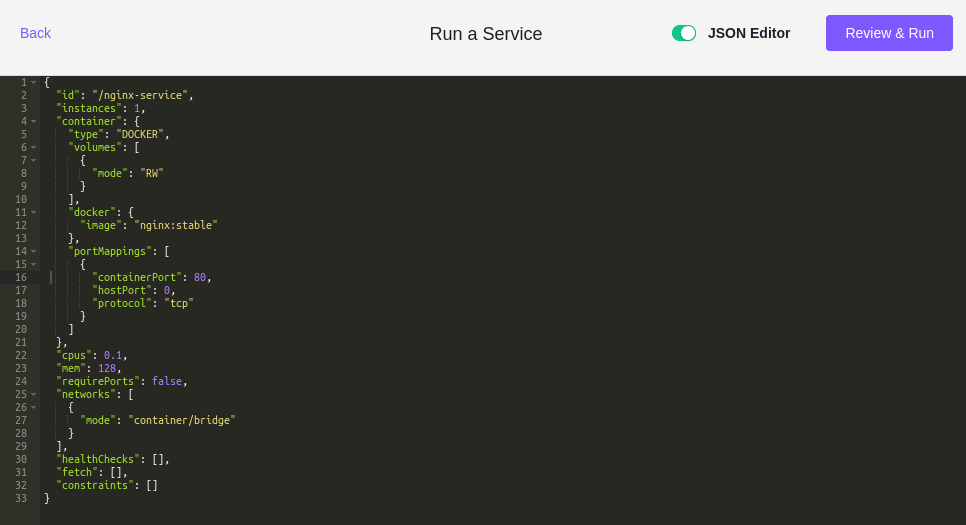
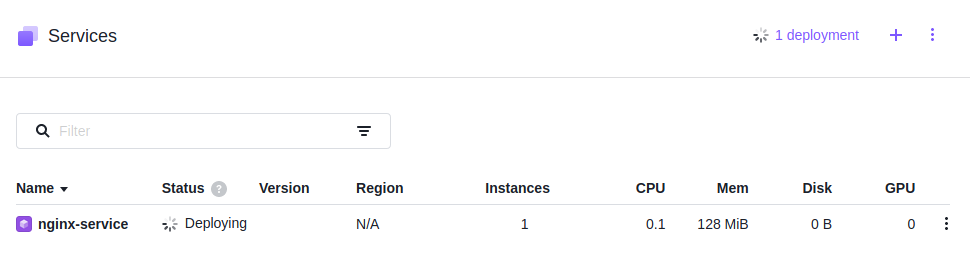
Run the service
After configuration, click “Review & Run“; After reviewing, click “Run service“. On “Services” panel, you will see the new service is being deployed and running.
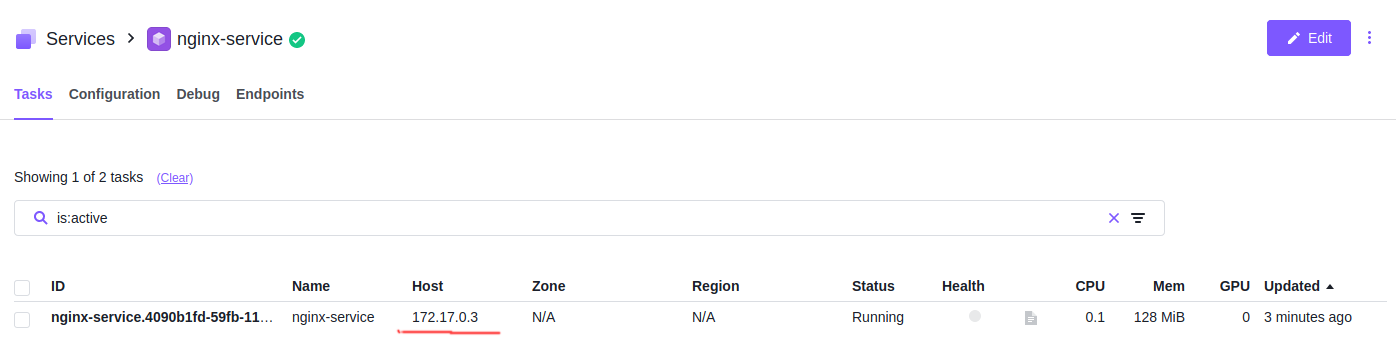
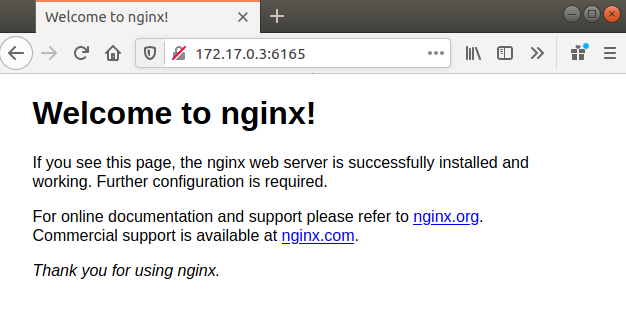
Now you will find the service runs on the private node (172.17.0.3) and the container’s 80 port was mapped to port 6165.
|
1 2 3 4 |
> docker exec -it dcos-e2e-default-f0bd1-agent-0 bash [root@dcos-e2e-default-f0bd1-agent-0 /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 22cad2bd70f9 nginx:stable "/docker-entrypoint.…" 12 minutes ago Up 12 minutes 0.0.0.0:6165->80/tcp mesos-6b61698d-b50b-4dda-8251-e275515d285d |
You can access this service through your browser.
Deploy the Service on Public Node
Deploying the service on private node is the default behavior. But if you want to expose the service on a public node, you need to add the following into the JSON configuration.
|
1 2 3 |
<span class="token property">"acceptedResourceRoles"</span><span class="token operator">:</span><span class="token punctuation">[</span> <span class="token string">"slave_public"</span> <span class="token punctuation">]</span><span class="token punctuation">,</span> |
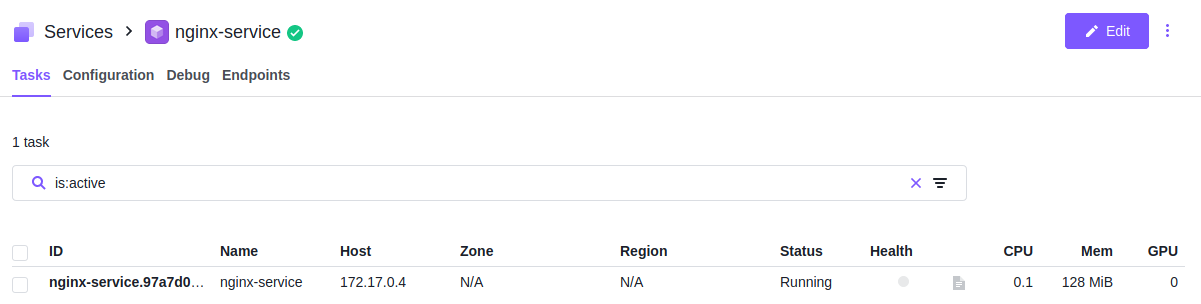
After updating the configuration and rerun the service, you will find the nginx service is running on the public node (172.17.0.4).
|
1 2 3 |
> docker exec dcos-e2e-default-8c975-public-agent-0 docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES d6f429c8e7cd nginx:stable "/docker-entrypoint.…" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 0.0.0.0:9134->80/tcp mesos-b031120a-3411-47fb-8440-07b9b48793bd |
But usually, the private node will have much more CPU core and memory than public node. We can use load balancer, such as Marathon LB, Edge LB (Enterprise Edition) to expose the services on public nodes, meanwhile the services are running on private nodes. I will talk about it in the next chapter.
Great! Now you have the first service running on DC/OS!


